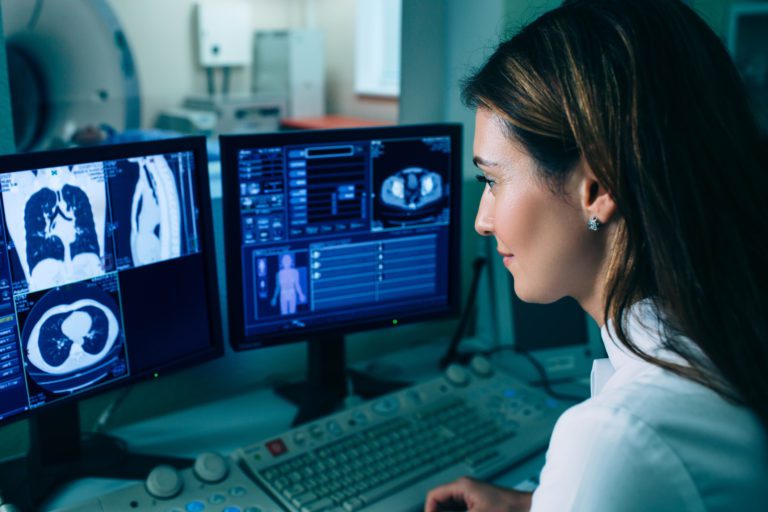
Plaque inside the arteries of your heart can grow and restrict blood flow to the muscles of the heart. Measuring calcified plaque with a coronary calcium scan may allow your doctor to identify potential coronary artery disease before you have signs and symptoms. The scan measures the amount of calcium and calcified plaque inside your coronary arteries.
These calcium deposits can help your doctor identify your potential risk of heart attacks and coronary artery disease. Your doctor will use your test results to determine if you may need medication or lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of heart attack or other heart problems.
Calcium cardiac scoring is a self-pay exam not covered by health insurance plans. Touchstone Imaging offers the test for $199, and you can use HSA and FSA funds to pay for it.
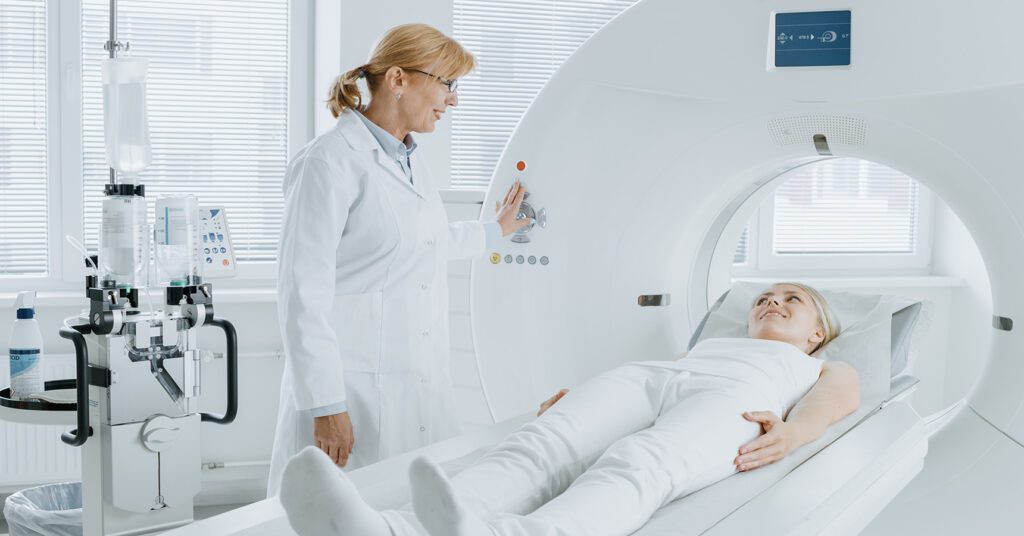
A cardiac scoring screening CT typically takes less than 15 minutes to complete at Touchstone Medical Imaging.
The screening test is considered appropriate for men over age 40 or women over age 50 who are at moderate risk for developing heart disease because of factors such as:
• Family or personal history of heart disease
• Past or present tobacco use
• History of high cholesterol, diabetes or high blood pressure
• Overweight or obesity
• High stress levels
• Inactive or sedentary lifestyle
Yes, the calcium cardiac scoring exam must be ordered by your physician.
Your calcium score indicates the level of plaque buildup.
0: No evidence of plaque; very low risk of heart attack in the near future.
1-10: Minimal evidence of plaque.
11-100: Mild evidence of plaque.
101-400: Moderate evidence of plaque.
Over 400: Extensive evidence of plaque, indicating significant coronary artery disease.
Your doctor will use this score to recommend lifestyle changes or medication to help lower your risk.
No special preparation is generally needed. However, you should avoid caffeine for at least four to 12 hours and refrain from smoking for four hours before your appointment.
The radiation level is low, comparable to a mammogram. While all radiation exposure carries a slight risk, the benefit of early and accurate detection of heart disease far outweighs it.