Phone:
Fax:
(210)614-1611
Hours

Tap services to view more information
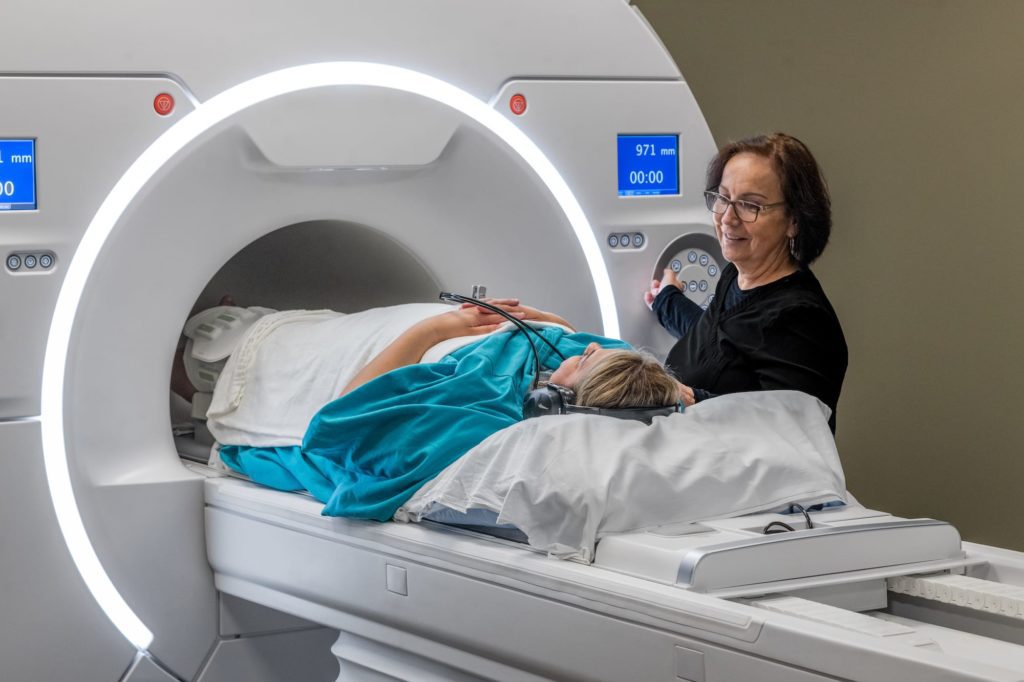
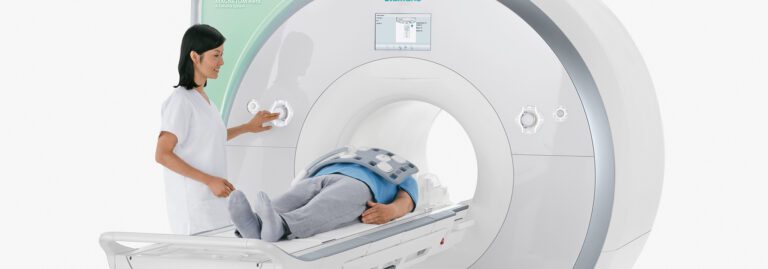
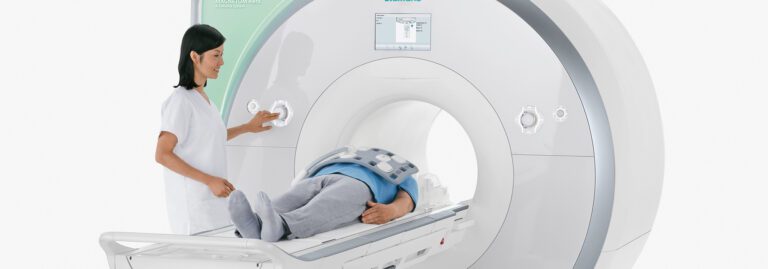
A 1.5T Highfield MRI offers a high tesla strength to produce images with great quality and highly-details allowing your physician to make an accurate diagnosis. A Highfield MRI machine is open on both ends and is flared on the sides to increase the magnetic strength and features a 60 inch opening. Our fastscan technology reduces imaging scan times without sacrificing image quality so patients can get their scan completed and back to their life quickly.
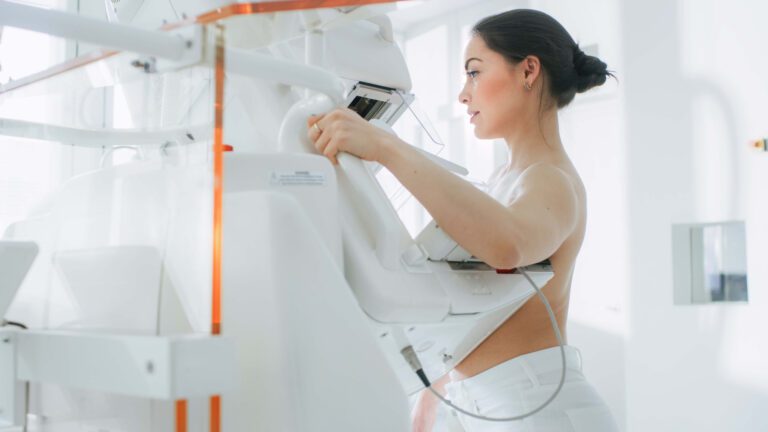
3D mammography, or tomosynthesis, is an advanced x-ray technology that takes multiple images of breast tissue to create a 3-dimensional picture of the breast. It differs from traditional mammography in that traditional mammography yields only a single image. A 3D image of the breast allows for better assessment of masses and reduces the likelihood of a false positive or an unnecessary biopsy.

An arthrogram provides more detailed information about your joints than a traditional x-ray, CT, or MRI can provide. A traditional scan can’t always pinpoint the problem because it is difficult to visualize some areas of the joint. An arthrogram is an imaging procedure that uses the injection of contrast in the joint and then uses x-ray, CT, or MRI to capture images that highlight various tissues in greater detail. Your provider is able to evaluate for small tears in tendons and ligaments or slight dislocations.
Coronary Calcium CT – also called Cardiac Scoring – measures calcified (hard) plaque inside the arteries that can grow and restrict blood flow to the muscles of the heart identifying potential Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) before you have symptoms.
A CT scan, also known as a CAT scan or Computed Tomography, is a special kind of X-ray that takes pictures of a cross-section of a part of your body. CT scan images provide more detailed information than traditional X-rays are able to. CT scans are used to quickly examine people who may have internal injuries and may be used to observe internal organs and tissues of the body to diagnose disease or injury.
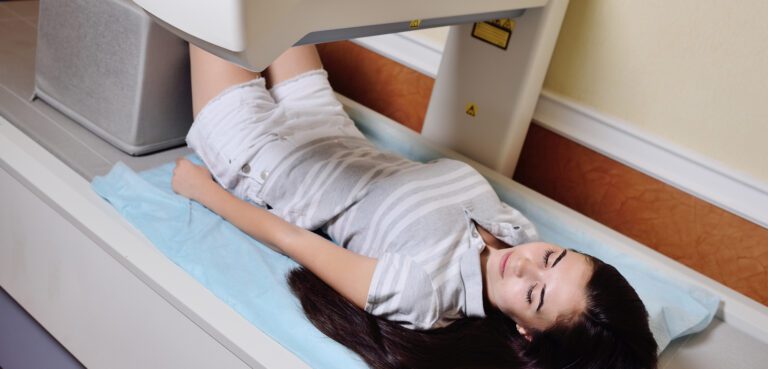
Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology that is used to measure bone loss, also known as osteoporosis. Because calcium in bones more readily accepts radio absorption, a bone scan easily identifies weakened areas and can measure the amount of calcium and other minerals in your bones and can detect stress fractures.
Fluoroscopy uses injected contrast dye and an X-Ray machine to take a continuous series of X-rays instead of individual snapshots. It is most commonly used to evaluate parts of your body that are moving in order to create a short video of your body system in motion. It is particularly useful for observing the digestive, urinary, respiratory, and reproductive systems and their functioning.
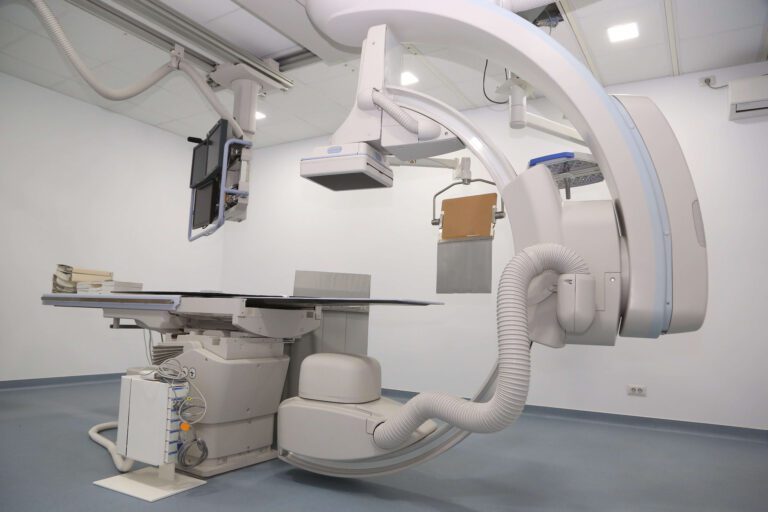
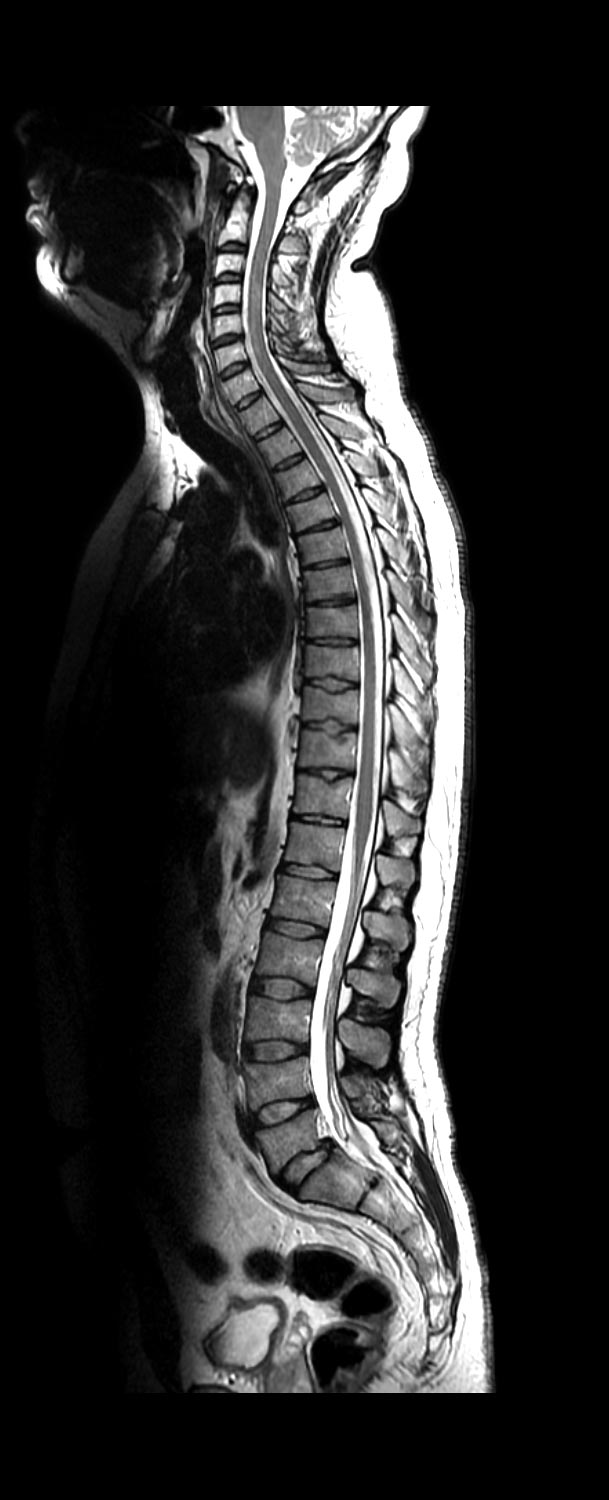
A myelogram is a specialized fluoroscopy, performed by a radiologist, that uses an injection of contrast medium into the space around the spinal cord to highlight the spinal cord and spinal nerves. A myelogram is particularly useful for those patients who cannot undergo an MRI for assessing spinal for disc abnormalities, nerve roots issues, and other spinal tissue concerns.

A PET/CT (Positron emission tomography) is a non-invasive exam that uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers to reveal how internal organs are functioning. The scan takes about 60 minutes and images are captured via CT as your body processes the radioactive material. This offers great insight into the root of the disease process or the source of symptoms.
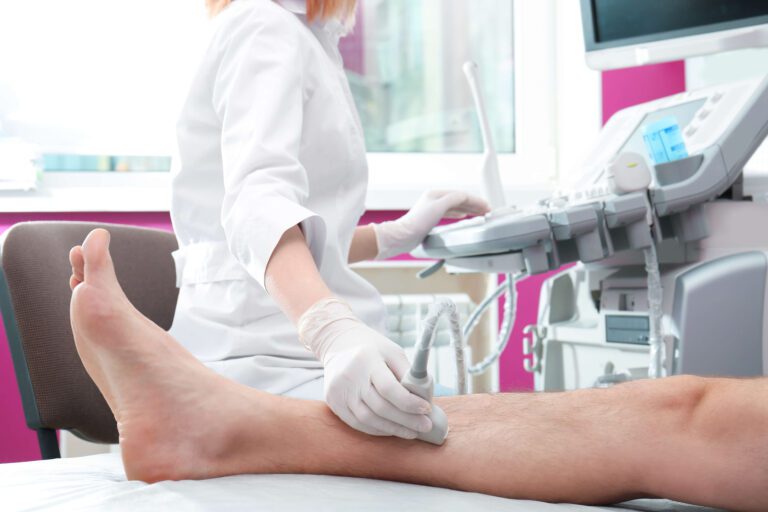
Ultrasound is a safe and painless procedure that is used to produce images of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. Ultrasounds are useful to scan internal organs, fetuses, and breast tissue.
An x-ray (radiograph) is a quick, painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Radiography involves exposing a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation called electromagnetic waves. The various body tissues absorb the radiation differently, creating different shades in an image to produce pictures of the inside of the body. Calcium in the bones absorbs radiation the most, so bones appear bright white while soft tissues absorb less and look gray. Air absorbs the least, so lungs and empty spaces appear black. X-rays are great for looking for broken bones or scarring in the lungs.


When your healthcare provider tells you they recommend a prostate MRI scan to help detect potential cancer early, you might be a little worried, but

Being told you need a low-dose lung CT scan can leave you with questions, especially if you’ve never had this type of scan before. Whether

Learn more about why your healthcare provider has recommended a CT angiogram, what the scan can help detect, what to expect, and how to be prepared.
Our patients say it best. Touchstone Imaging provides welcoming, comforting outpatient facilities with friendly and helpful staff.





To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior to provide a better user experience. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.