You’ve talked with your healthcare provider about getting a lung CT scan to check for COPD, but you’re feeling a little overwhelmed, and you still have questions. We’re here to help you.
Your lung CT scan is crucial to diagnosing lung and breath conditions like COPD. It helps your doctors decide what are the best solutions and plan of care for your particular health situation.
In this guide, we’ll look at the essentials of the scan, and at your experience during a lung CT scan. You’ll learn everything you need to know to make your scan worry-free and comfortable
What is a lung CT scan?
A lung CT scan, or a computed tomography scan of the lungs, is a specialized imaging technique that offers detailed, cross-sectional views of your lungs.
By capturing multiple images from various angles, the CT scan assembles a comprehensive picture of your lungs.
These images enable your healthcare provider to observe the intricate structures within the lungs that might remain undetected with other imaging methods.
What happens during a lung CT?
When you have a lung CT scan, you’ll generally lie on your back on a table that smoothly slides into the CT scanner, a large, doughnut-shaped machine.
Before the scan begins, you might be asked to raise your arms above your head to ensure an unobstructed view of your lungs. As the scanner operates, it rotates around your chest area, specifically focusing on capturing images of your lungs.
While the machine is collecting these images, you may be asked to hold your breath for short intervals to prevent any movement of the lungs, ensuring optimal image clarity. It’s important to remain as still as possible throughout the scan.
You’ll hear the machine making whirring or buzzing sounds, but rest assured, the scan is painless and non-invasive.
Why did my provider choose a CT scan?
Lung CT scans stand out among other imaging techniques due to their ability to offer high-resolution images of lung tissues, blood vessels, and airways. These detailed images enable detection of even minor abnormalities or changes within the lungs.
Since COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) involves damage to the small airways and air sacs in the lungs, such detailed imaging becomes paramount.
Recognizing specific problematic areas aids healthcare providers in delivering precise diagnoses and formulating appropriate treatment strategies.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with a lung CT scan?
The primary concern for a lung CT scan is the exposure to a minimal amount of radiation.
The radiation from a CT scan is typically minimal and is widely regarded as safe for most individuals. If there are concerns, it’s essential to have an open dialogue with your healthcare provider.
If contrast material is used during the scan to enhance the images, there’s a small possibility of allergic reactions in some individuals. These reactions can range from mild sensations like warmth or itchiness to more uncommon allergic reactions. Always inform your healthcare provider of any allergies or past reactions to contrast dyes or materials.
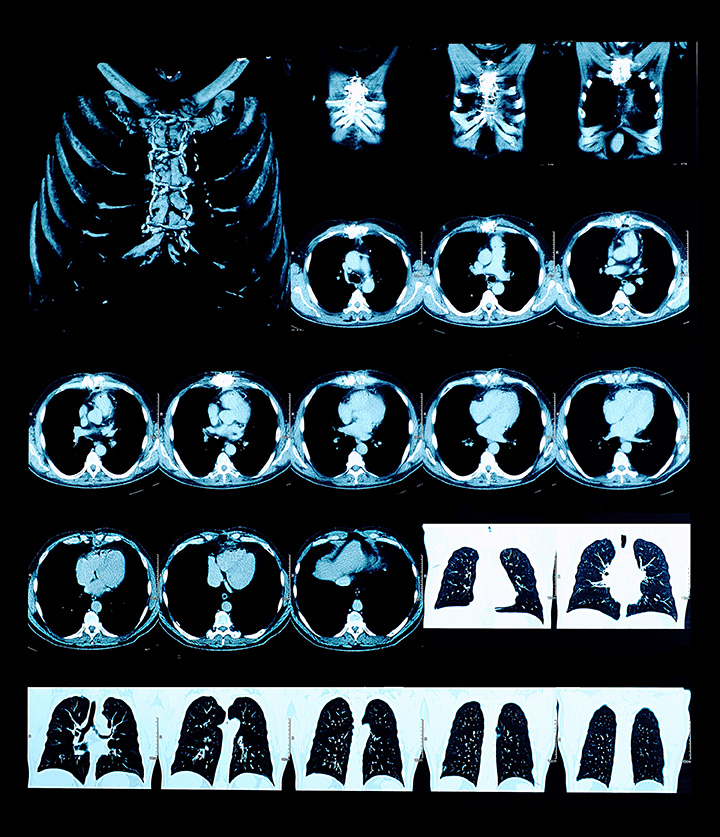
Understanding COPD
COPD is a chronic respiratory disease that hinders airflow from the lungs. It’s primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritating gasses or particles, most often from tobacco smoke.
People who smoke or have smoked in the past are at a higher risk, but exposure to certain workplace dust, chemicals, or frequent lower respiratory infections during childhood can also contribute to its development.
The disease results from a combination of bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchial tubes) and emphysema (damage to the lungs’ air sacs), making breathing a significant challenge over time.
What are the main symptoms and stages of COPD?
COPD presents with a variety of symptoms, which generally become more severe as the disease progresses. Early signs include a persistent cough that may produce mucus, shortness of breath, especially during physical activities, and frequent respiratory infections.
As COPD advances, symptoms might also encompass wheezing, fatigue, chest tightness, and unintended weight loss.
COPD is categorized into four stages, ranging from mild to very severe:
- Mild COPD: Individuals may have a chronic cough and produce more mucus than usual but may not notice any other symptoms.
- Moderate COPD: Shortness of breath may start to become noticeable, especially after exertion.
- Severe COPD: Breathing difficulties become more prevalent and can interfere with everyday activities. Flare-ups, or exacerbations, might happen more frequently.
- Very Severe COPD: At this stage, breathing issues are present even during rest and can be life-threatening. Exacerbations are more common and can be severe.
Why is early detection of COPD crucial?
Identifying COPD in its early stages is vital for several reasons. Firstly, early detection can help slow the progression of the disease with the right interventions.
While there’s currently no cure for COPD, treatments, lifestyle changes, and therapies can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Furthermore, recognizing COPD sooner rather than later can prevent potential complications, such as heart problems, lung infections, or respiratory failure.
A lung CT scan plays an instrumental role in early detection, as it offers detailed images of lung tissue, helping healthcare providers pinpoint any abnormalities or changes indicative of COPD even before severe symptoms appear.
How COPD affects your lungs
COPD brings about multiple changes in the lungs. The airways and tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs lose their elasticity, becoming overstretched.
As a result, the walls between many of the air sacs get destroyed, leading to the formation of larger but fewer air sacs.
Meanwhile, the walls of the airways become thick and inflamed. Mucus production in the airways can increase, which can further block the narrowed passages.
How do these changes impact lung function?
All these alterations have a direct and detrimental impact on how your lungs function. The loss of elasticity and the damage to the air sacs make it harder for the lungs to expand and contract effectively, hindering the efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
As the airways become narrowed and obstructed with mucus, airflow gets restricted. In turn, breathing becomes more laborious. People with COPD often experience difficulty exhaling fully, which means stale air remains trapped in the lungs, reducing their capacity for fresh, oxygen-rich air.
Why is it important for my provider to see these changes?
Seeing the extent of damage and where it’s located can provide a clearer picture of the severity of the condition, which helps your provider determine the most suitable treatment path.
A lung CT scan can offer detailed and clear images of the lungs, allowing healthcare providers to identify any changes, such as the thickening of airway walls, the destruction of air sacs, and any unusual mucus build-up.
Additionally, by getting a visual insight into the lungs’ condition, it allows both the individual and the healthcare provider to better understand and manage the disease.

How does the progression of COPD affect the lungs over time?
Over time, if COPD progresses without appropriate intervention, the damage to the lungs can become more extensive.
The initial symptoms like occasional shortness of breath and mucus production might evolve into constant breathing challenges, even during rest. The lung tissue may continue to lose its elasticity, and more air sacs might get destroyed.
As the condition advances, the body is challenged to receive the oxygen it needs, leading to further complications such as fatigue, swelling in limbs, and decreased tolerance to physical activities.
The progressive nature of COPD underscores the significance of timely diagnosis, and a lung CT scan serves as a pivotal tool in this journey, capturing the lungs’ condition at various stages and assisting in informed medical decisions.
How CT scans detect COPD
A lung CT scan provides detailed, cross-sectional images of the lungs. These images can be thought of as slices that, when pieced together, give a comprehensive picture of the lung’s structure and any abnormalities.
In the case of COPD, the CT scan can reveal several indicative changes:
- Emphysema: COPD often leads to the destruction of the walls of the air sacs (alveoli), resulting in larger air spaces rather than many tiny ones. The scan can highlight these enlarged spaces, indicating emphysema, a component of COPD.
- Airway wall thickness: Thickened airway walls, another sign of COPD, can be effectively spotted on a CT scan. This thickening can result from chronic inflammation, common in COPD.
- Mucus obstructions: The scan can also visualize mucus blockages in the smaller airways, indicative of chronic bronchitis, another aspect of COPD.
Why is a CT scan more accurate than other methods in detecting COPD?
Lung CT scans offer a level of detail and clarity that many other imaging methods can’t match. The high-resolution images allow healthcare providers to see even minor changes in the lungs’ structure, making it easier to spot the early signs of COPD.
By looking at the combination of emphysematous changes, airway wall thickness, and mucus blockages, healthcare providers can get a more accurate picture of whether or not a person has COPD. This precision aids in both diagnosis and the assessment of disease severity, enabling tailored treatment plans based on individual needs.
Can a CT scan differentiate between COPD and other lung diseases?
Yes, a lung CT scan is great at differentiating between COPD and other lung diseases. While certain lung conditions might have overlapping symptoms or even some similar visual indications, the CT scan’s detailed imagery helps pinpoint the specific abnormalities and patterns unique to each disease.
For instance, while both COPD and pulmonary fibrosis might present with shortness of breath, the visual characteristics on a CT scan are distinct. COPD might show the previously mentioned emphysematous changes and airway thickening, while pulmonary fibrosis would exhibit scarring and a honeycomb-like pattern in the lungs.
Lung CT scans not only help in diagnosing COPD but also ensure that other lung conditions are accurately identified or ruled out.
Your lung CT results
After your lung CT scan, a specialized physician known as a radiologist will analyze the acquired images. Radiologists are trained to interpret the intricate details of CT scans and to identify abnormalities or changes in the lung’s structure.
The radiologist will provide a detailed report of their findings to your healthcare provider, who will then discuss the results with you and elaborate on the next steps, if any, based on those findings.
What features on the CT scan indicate the presence or absence of COPD?
A lung CT scan can reveal several features that are indicative of COPD, and the radiologist will look for specific patterns and anomalies in the lung tissue and airways.
This includes the presence of emphysema, as well as chronic inflammation, and chronic airway blockages due to bronchitis.
The absence of such features in your results, or the presence of different patterns, may indicate that COPD is not present––or it may point towards other respiratory conditions.
How can a healthcare provider use a CT scan to make a treatment plan for COPD?
Once the results of the lung CT scan are in, your healthcare provider can use the detailed images and the radiologist’s report to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
The specific changes noted in the scan, like the degree of airway obstruction or the extent of changes due to emphysema, will guide the healthcare provider in recommending the most suitable therapies, lifestyle modifications, and potentially, medications. For instance, if extensive mucus blockage is observed, medications to clear the airways may be prescribed.
The goal is to tailor the treatment plan to your unique needs and to address the specific manifestations of COPD revealed by the CT scan, aiming to manage symptoms effectively and enhance your quality of life.
How to schedule your CT lung scan appointment with us
Touchstone Medical Imaging offers CT scans in Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Montana, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Reach out to us at Touchstone, and we’ll help you schedule a mammogram appointment at an imaging center near you, today.
We’re here to help you get the answers you need.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about COPD and Lung CT Scans
A lung CT scan is a detailed imaging method of the lungs, often chosen because of its accuracy in visualizing lung structures and conditions.
During a lung CT, you’ll lie on a table that slides through a doughnut-shaped machine, which captures detailed images of your lungs.
Yes, while generally safe, a lung CT scan exposes you to a small amount of radiation, and there’s a rare risk of allergic reaction to contrast agents if used.
COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is a progressive lung disease caused mainly by smoking and exposure to harmful pollutants, leading to breathing difficulties.
A: COPD causes inflammation, narrowing of the airways, and damage to lung tissue, which impairs airflow and reduces the lungs’ ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Early detection of COPD allows for prompt treatment, which can slow disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall quality of life.
A CT scan provides high-resolution images that can reveal specific structural changes in the lungs, enabling healthcare providers to differentiate between COPD and other lung diseases.
The findings on your CT scan can help your healthcare provider tailor a treatment plan for COPD, addressing the severity of the disease and specific lung changes observed.